KW Micro Power cut the weight of their compact turbogenerator by 44% with nTop
See how KW Micro Power used nTop to design a lightweight multifunctional microturbine housing with embedded cooling channels.
Applications
Key Software Capabilities
- Integrations
- Simulation
Summary
KW Micro Power used nTop to redesign the housing of their aerospace-grade, high-power-density, compact turbogenerator for metal additive manufacturing. Using Field Optimization and shelling, they reduced the housing’s weight by 44% and reduced the temperature by 33%.

About: KW Micro Power designs and manufactures high-power-density Auxiliary Power Units (APUs) for commercial aviation and military applications. Over the past five years, Enrique Enriquez, the president of KW Micro Power, created a microturbine generator roughly the size of a microwave oven that can crank out more power than systems 10 times as large.
- Industry: Aerospace and defense
- Size: <25 employees
- Location: Hialeah, Florida, USA
- Product: Multifunctional microturbine housing with embedded cooling channels
The project
Design a critical component of KW Micro Power’s airborne microturbine: the generator housing

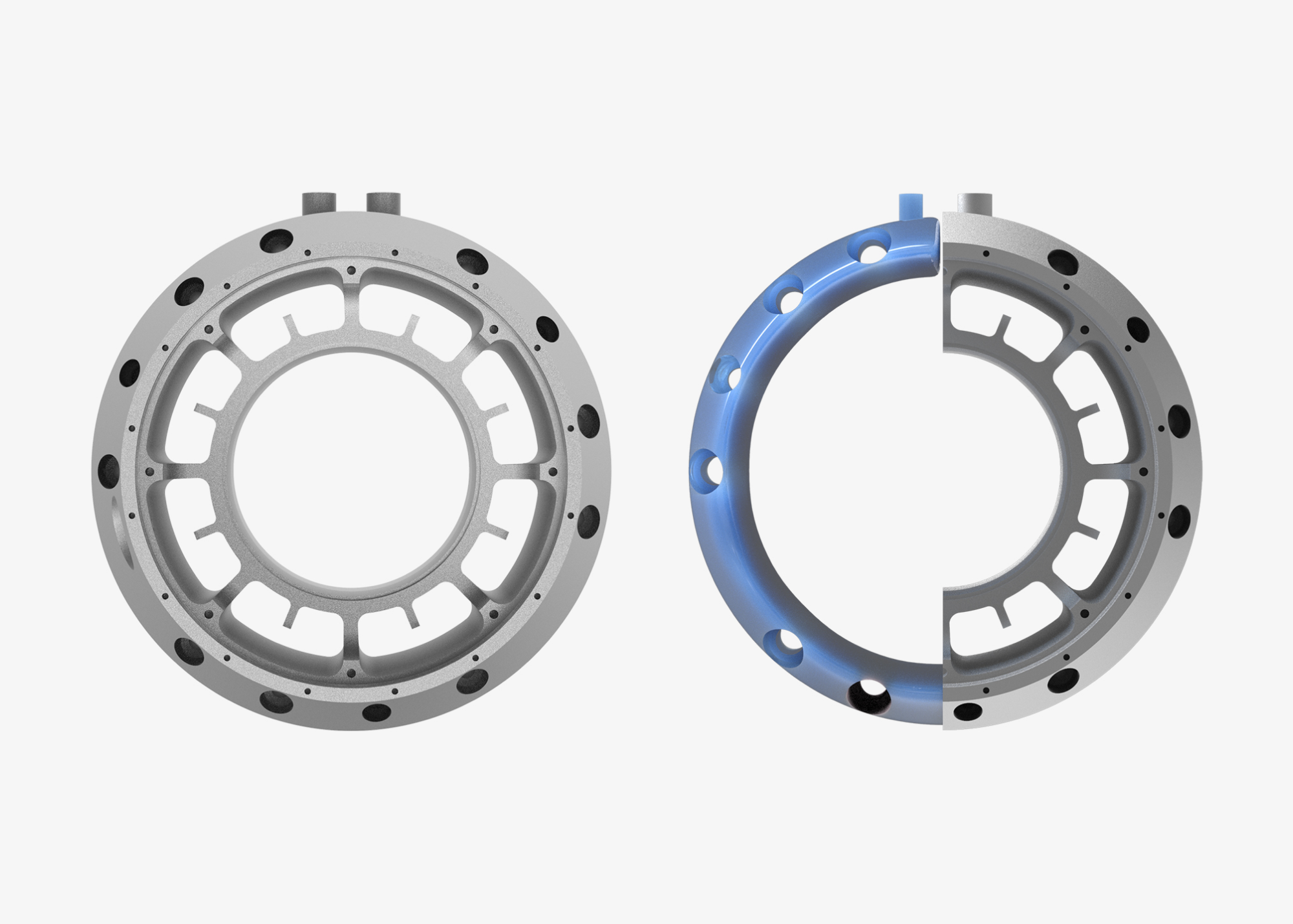
The engineers of KW Micro Power, nTop, and VELO3D created a housing that is not only much lighter than the original design and manufacturable as one piece with minimal support structures but also features internal conformal channels for cooling the engine and preheating the fuel.
The challenge
Create a lighter APU with more efficient thermal management
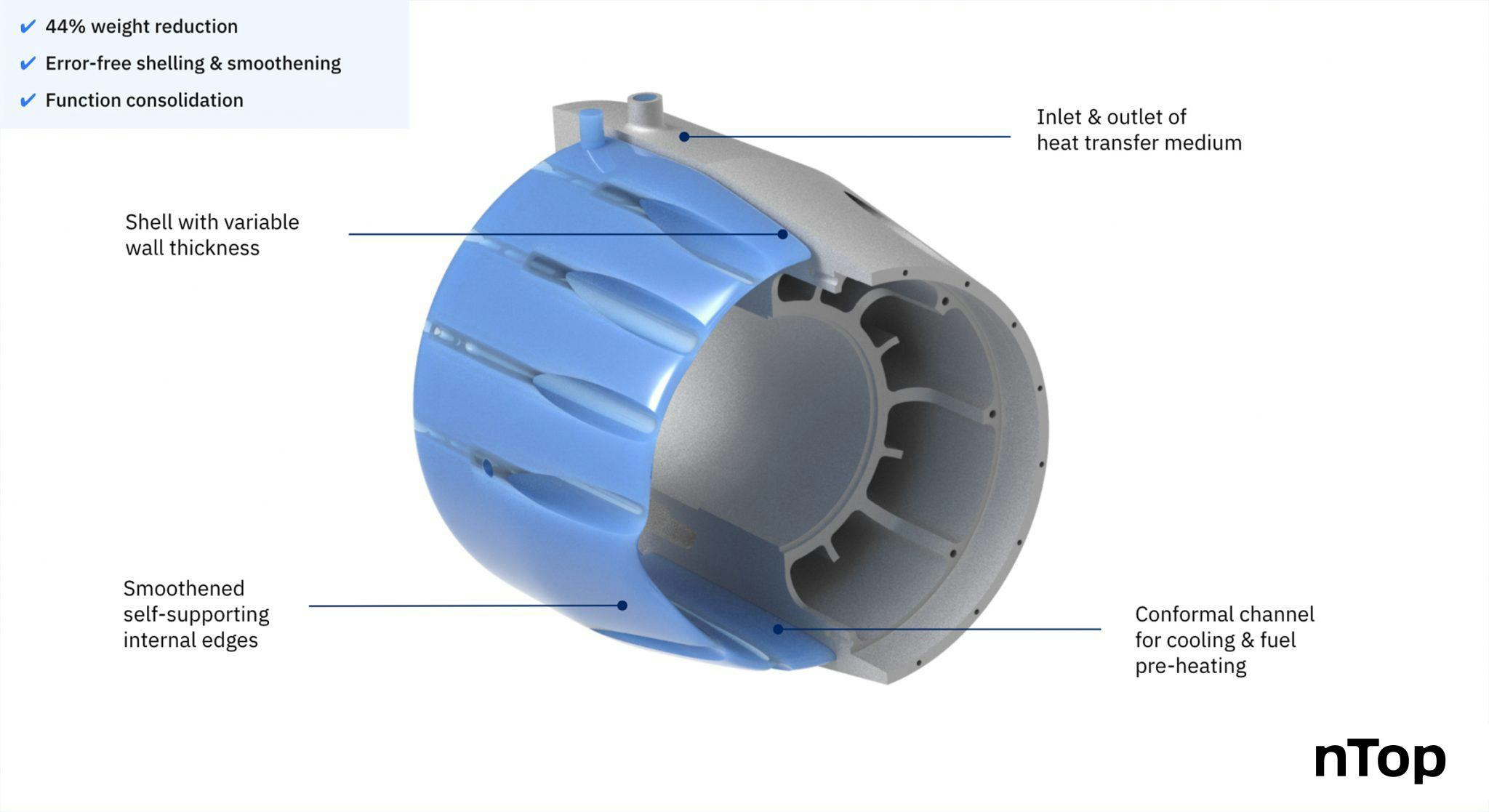
The redesigned microturbine generator housing. It features a conformal cooling channel created using variable shelling and automated smoothening.
For APUs on an aircraft or drone, lightweighting is a top priority.
Cooling was also a challenge. In fact, thermal management is one of the main size constraints of electric machines.
Simply put, better cooling means more power.
The solution
Redesign the APU for additive manufacturing with nTop
Enriquez’s team followed a Field-Driven Design approach:
They first confirmed that the loads on the housing were relatively small using nTop's integrated static and modal analysis simulation tools. Then they removed unnecessary material to create a hollow shell with a variable wall thickness. Finally, they smoothed the internal geometry to ensure that it required no support structures during manufacturing with VELO3D’s metal AM process.
As for thermal management, KW Micro Power incorporated multiple functions into one component. The hollow structure initially conceived to reduce the motor casing’s weight could also function as a cooling channel.
The team evaluated the effect of the conformal cooling channels on the performance of the system through simulations. They combined results from thermal FE analysis in nTop with CFD simulations in Ansys Fluent.
The results
44%
weight reduction
33%
temperature reduction
3
functions in a single part
Why nTop?
Lightweighting
The engineering team managed to reduce the generator’s housing weight by 44% — from approximately 10.4 kg down to 5.9 kg.
The entire process of redesigning the part for additive manufacturing required only a few simple design blocks in nTop. They performed the task almost instantaneously without errors and took less than a day’s work to design a lighter part in only one piece. It also opened up opportunities to add functionality: conformal cooling channels for heat management.
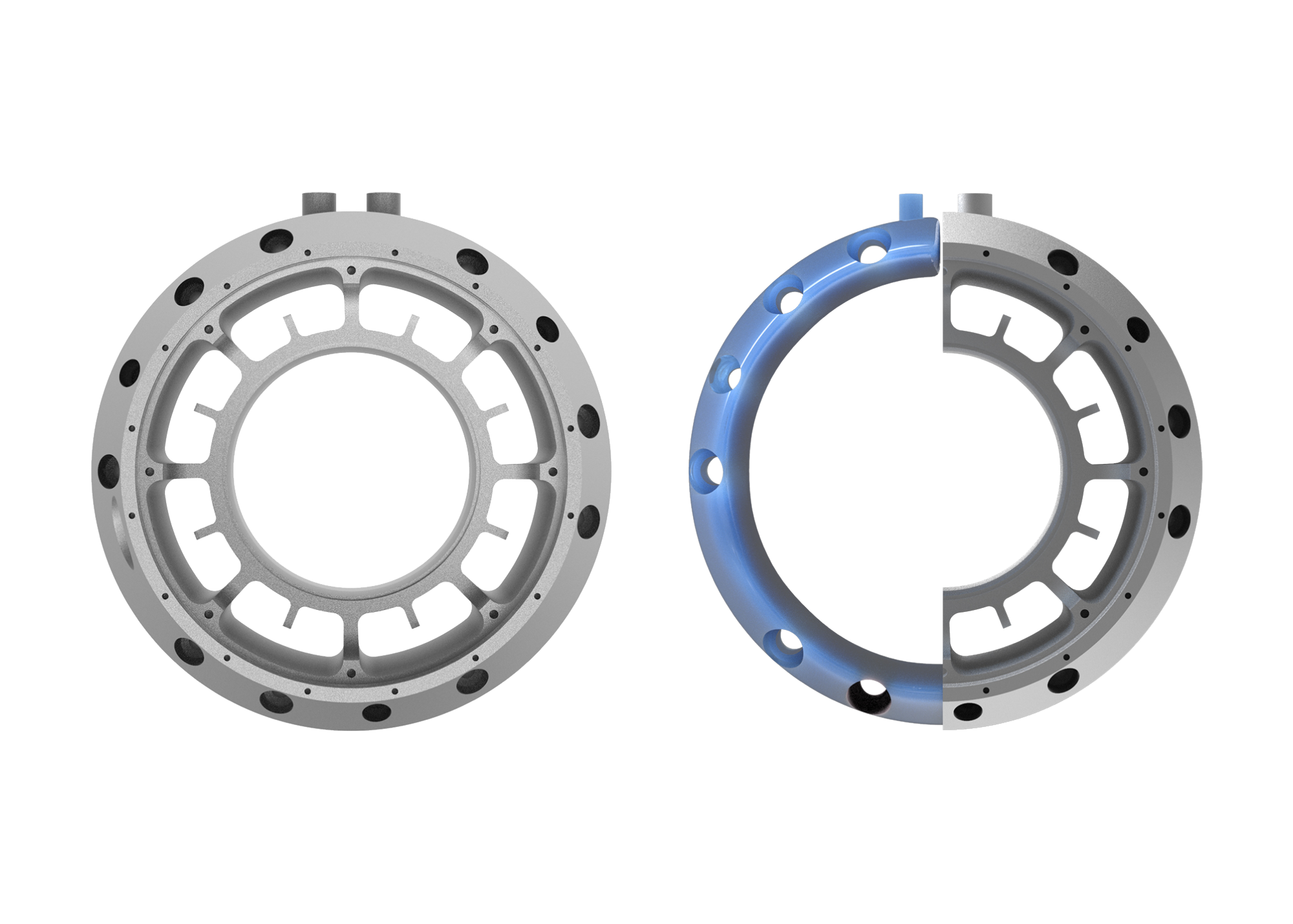
The redesigned housing took less than a day to design.
Thermal management
Thanks to conformal cooling channels designed in nTop, KW Micropower achieved a 33% drop in maximum temperature and an 86% drop in the generator’s external temperature. This made the part safe to touch.
This temperature drop allowed the use of aluminum as the material for the generator housing. Without the conformal cooling channels, KW Micro Power would potentially be forced to use a material with higher thermal resistance — increasing costs — or run their generator at lower speeds — throttling its power output.
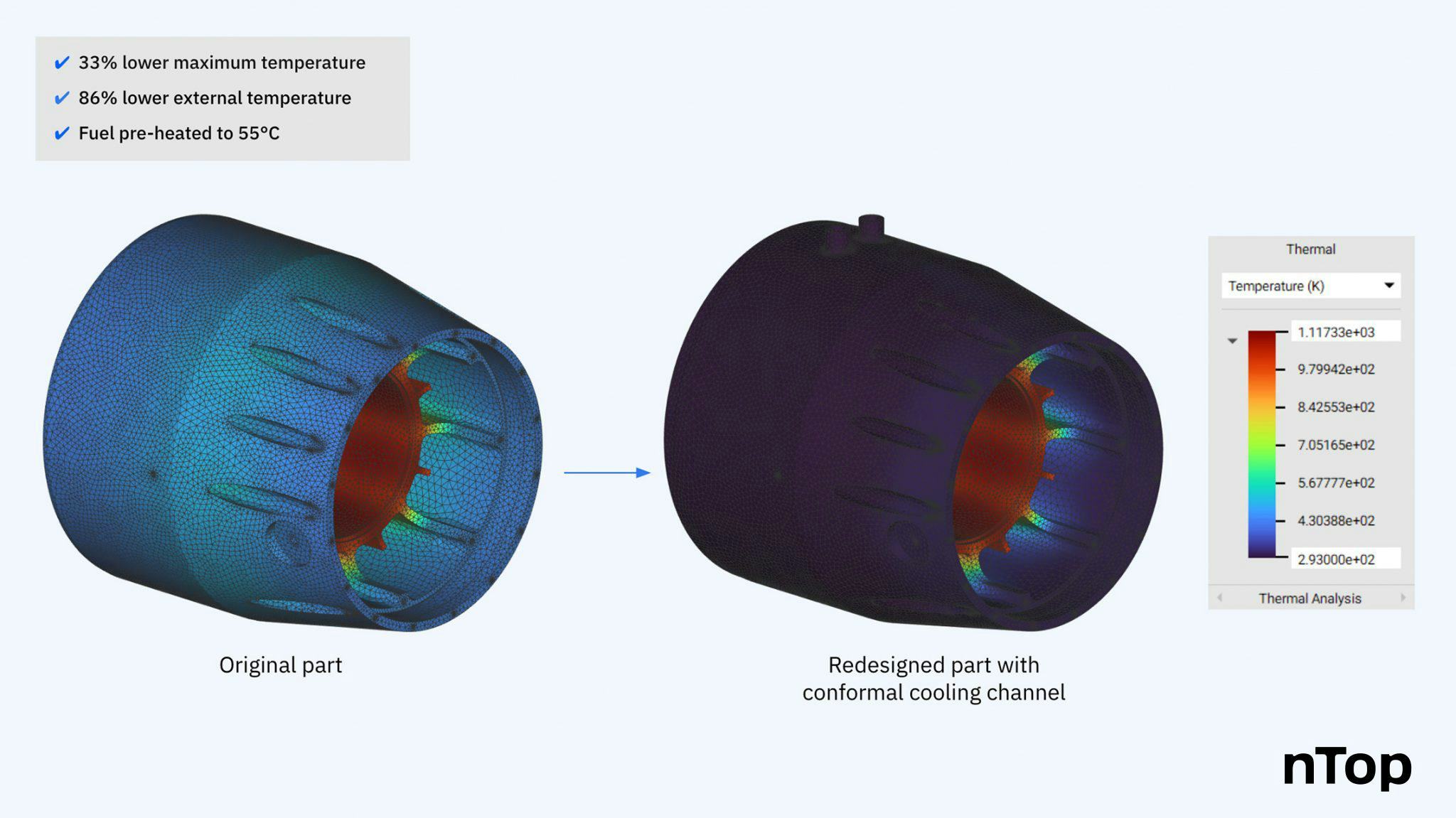
Thermal analysis results of the microturbine generator housing carried out in nTop.
From design to manufacturing
VELO3D manufactured the new generator housing on the Sapphire metal 3D printing system.
VELO3D’s additive manufacturing capabilities were considered during the design phase to create a manufacturable part with minimal support structures and post-processing requirements.
VELO3D’s SupportFree technology and tight control of processing parameters were an excellent match for nTop’s unparalleled level of control, easing the transition from product development to manufacturing.
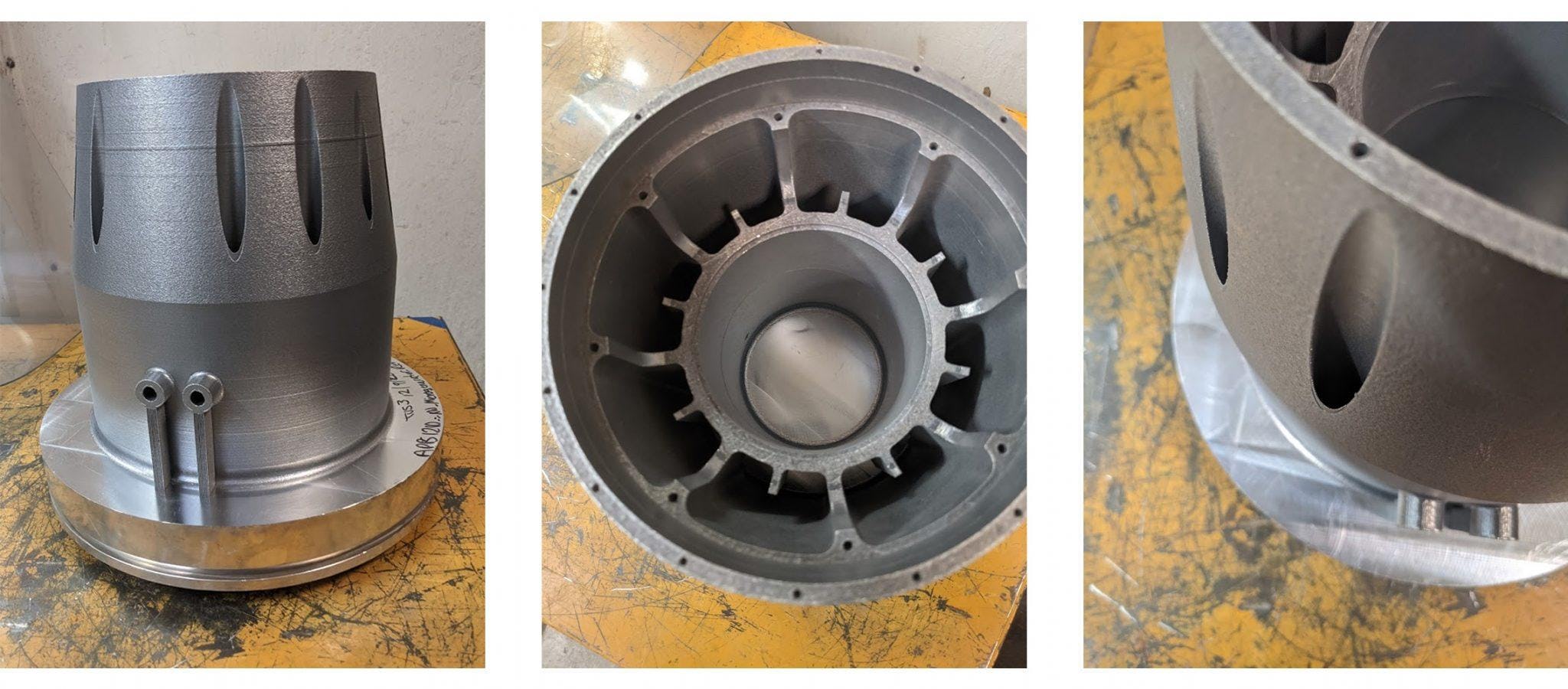

The manufactured microturbine generator housing
Conclusion
KW Micro Power redesigned the housing of their aerospace-grade, high-power-density, compact turbogenerator for metal Additive Manufacturing. Using nTop, they reduced its weight by 44% for a total savings of 4.5 kg.